What is Agile Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
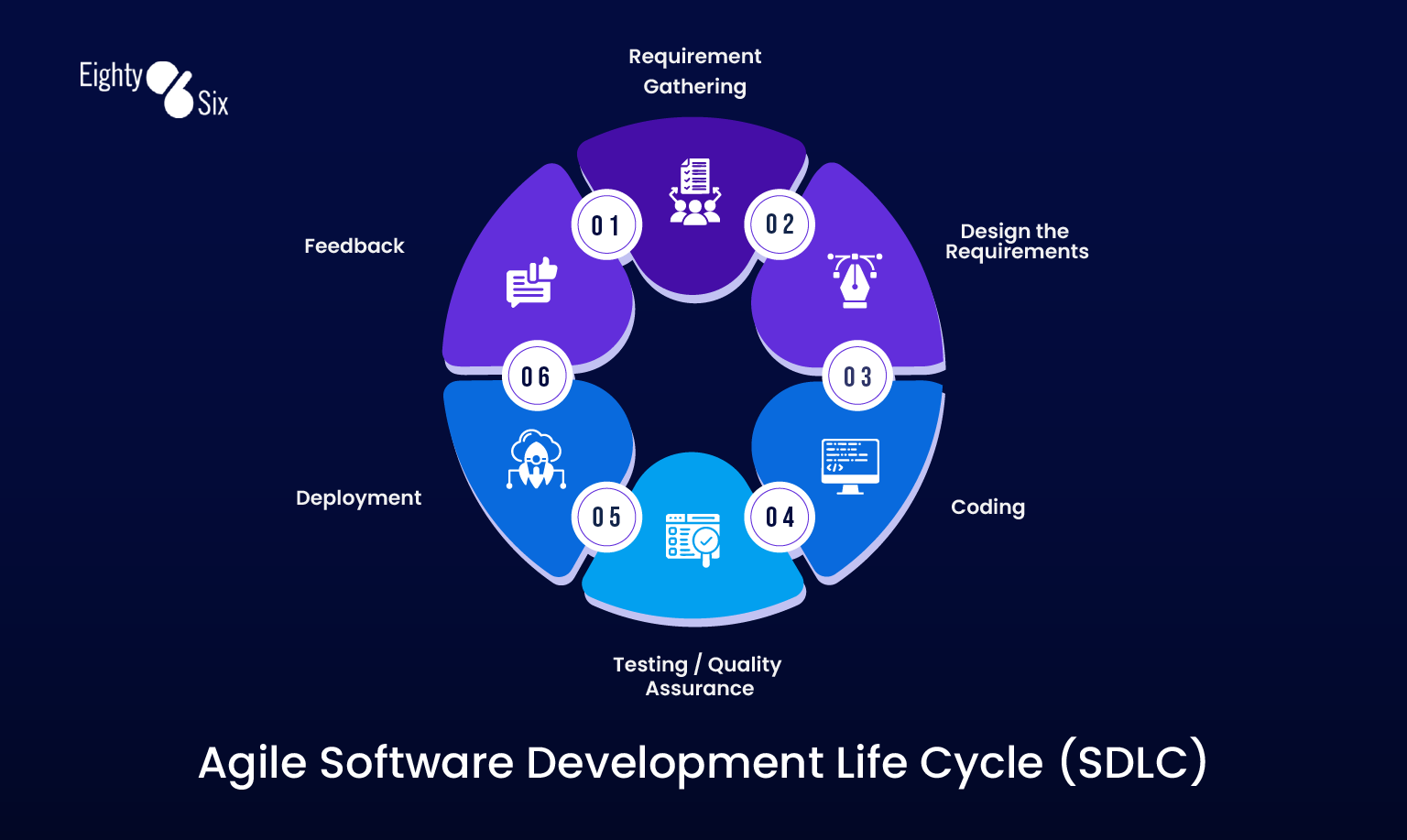
Table of contents
Introduction to Agile and SDLC
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) represents the structured process of creating software applications from conception to deployment and maintenance. Traditionally, SDLC followed rigid, sequential approaches that often resulted in delayed delivery and inflexible solutions.
Agile methodology revolutionized this landscape by introducing iterative, flexible, and collaborative approaches to software development. Born from the Agile Manifesto in 2001, this methodology prioritizes individuals and interactions over processes and tools, working software over comprehensive documentation, customer collaboration over contract negotiation, and responding to change over following a plan.
The integration of Agile principles with SDLC has created a powerful framework that enables teams to deliver high-quality software faster while maintaining flexibility to adapt to changing requirements. This approach has become the gold standard for modern software development, with over 71% of organizations worldwide adopting some form of Agile methodology.
What is Agile Development SDLC?
Agile Development SDLC is an iterative and incremental approach to software development that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and rapid delivery of working software. Unlike traditional waterfall models, the Agile software development life cycle breaks down the development process into smaller, manageable iterations called sprints or iterations.
Key characteristics of Agile SDLC include:
- Iterative Development: Work is completed in short cycles (typically 1-4 weeks)
- Continuous Feedback: Regular input from stakeholders and end users
- Adaptive Planning: Plans evolve based on learning and changing requirements
- Cross-functional Teams: Collaborative approach involving diverse skill sets
- Working Software: Focus on delivering functional software over extensive documentation
The Agile process in software development emphasizes continuous improvement, allowing teams to learn from each iteration and apply those insights to subsequent cycles. This approach significantly reduces project risks while ensuring that the final product meets user expectations and business objectives.
Phases of SDLC in Agile Methodology
The SDLC phases in Agile methodology follow a cyclical pattern that repeats throughout the project lifecycle. Each phase flows seamlessly into the next, creating a continuous development cycle:1. Requirements Gathering and Analysis
In Agile, requirements are gathered continuously rather than upfront. This phase includes:- User Story Creation: Requirements are written as user stories that describe functionality from the user’s perspective
- Backlog Prioritization: Features are ranked based on business value and urgency
- Acceptance Criteria Definition: Clear criteria for when a feature is considered complete
- Stakeholder Collaboration: Ongoing communication with business stakeholders
2. Design and Architecture
Agile design focuses on creating flexible, scalable solutions:- Evolutionary Design: Architecture evolves with each iteration
- Minimum Viable Design: Start with essential design elements
- Collaborative Design Sessions: Cross-functional teams contribute to design decisions
- Prototyping: Quick prototypes to validate design concepts
3. Development and Coding
The development phase emphasizes rapid, high-quality code delivery:- Sprint Development: Code is written in short, focused sprints
- Pair Programming: Developers work together to improve code quality
- Test-Driven Development (TDD): Tests are written before code implementation
- Continuous Integration: Code is integrated frequently to avoid conflicts
4. Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing in Agile is integrated throughout the development process:- Continuous Testing: Testing occurs throughout each sprint
- Automated Testing: Automated test suites ensure rapid feedback
- User Acceptance Testing: Regular validation with end users
- Exploratory Testing: Manual testing to discover unexpected issues
5. Deployment and Release
Agile deployment strategies focus on frequent, reliable releases:- Continuous Deployment: Automated deployment pipelines
- Feature Flags: Gradual rollout of new features
- Rolling Updates: Zero-downtime deployment strategies
- Monitoring and Feedback: Real-time system monitoring
6. Maintenance and Support
Post-deployment activities include:- Continuous Monitoring: System performance and user behavior analysis
- Bug Fixes: Rapid response to issues
- Feature Enhancements: Ongoing improvements based on user feedback
Agile vs Traditional SDLC (Waterfall Model Comparison)
Understanding the differences between Agile methodology vs SDLC traditional approaches is crucial for making informed development decisions:
Aspect | Agile SDLC | Traditional SDLC (Waterfall) |
Approach | Iterative and incremental | Sequential and linear |
Flexibility | High adaptability to changes | Limited flexibility after requirements phase |
Customer Involvement | Continuous collaboration | Limited to requirements and final testing |
Risk Management | Early risk identification and mitigation | Risks discovered late in the process |
Documentation | Just enough documentation | Comprehensive documentation |
Testing | Continuous testing throughout development | Testing phase after development completion |
Delivery Time | Frequent releases (weeks/months) | Single final release (months/years) |
Team Structure | Cross-functional, self-organizing teams | Specialized, hierarchical teams |
Project Visibility | High transparency with regular demos | Limited visibility until final delivery |
Change Management | Embraces change as competitive advantage | Changes are costly and discouraged |
The Agile vs SDLC comparison clearly shows why modern organizations prefer Agile approaches for their software development projects.
Benefits of Agile in SDLC
The benefits of Agile in SDLC are numerous and significant, making it the preferred choice for modern software development:
Speed and Time-to-Market
- Faster Delivery: Working software is delivered in weeks rather than months
- Early Value Realization: Customers can start using features as they’re completed
- Reduced Time-to-Market: Competitive advantages through rapid deployment
Flexibility and Adaptability
- Change Accommodation: Easy adaptation to changing requirements
- Iterative Improvement: Continuous refinement based on feedback
- Market Responsiveness: Quick pivots based on market conditions
Enhanced Collaboration
The focus on collaborative software development brings multiple advantages:
- Cross-functional Teams: Better communication and knowledge sharing
- Stakeholder Engagement: Regular involvement of business stakeholders
- Transparent Communication: Open channels between all team members
Risk Reduction
- Early Problem Detection: Issues are identified and resolved quickly
- Incremental Risk Assessment: Risks are managed throughout the project
- Reduced Project Failure Rate: Higher success rates compared to traditional methods
Improved Quality
- Continuous Testing: Quality is built into every iteration
- Regular Feedback: Constant validation ensures user satisfaction
Common Agile Frameworks Used in SDLC
Several Agile frameworks in SDLC have gained popularity, each offering unique approaches to implementing Agile principles:
Scrum
Scrum is the most widely adopted Agile framework:
- Sprint Structure: Work organized in 1-4 week sprints
- Scrum Roles: Product Owner, Scrum Master, Development Team
- Scrum Events: Sprint Planning, Daily Standups, Sprint Review, Retrospective
- Scrum Artifacts: Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, Product Increment
Kanban
Kanban focuses on visual workflow management:
- Visual Boards: Work items displayed on Kanban boards
- Work-in-Progress Limits: Controls on concurrent work items
- Continuous Flow: Work moves continuously through the pipeline
- Pull System: Team members pull work when ready
Extreme Programming (XP)
XP emphasizes technical excellence:
- Pair Programming: Two developers working on one workstation
- Test-Driven Development: Tests written before code
- Continuous Refactoring: Regular code improvement
- Simple Design: Minimal complexity in system design
Lean Development
Lean focuses on eliminating waste:
- Value Stream Mapping: Identifying and optimizing value delivery
- Waste Elimination: Removing non-value-adding activities
- Continuous Improvement: Kaizen principles applied to development
- Just-in-Time: Delivering exactly what’s needed when needed
Understanding agile methodology advantages helps teams choose the right framework for their specific needs.
Real-World Examples of Agile SDLC Implementation
Spotify: Scaling Agile Culture
Spotify has become synonymous with successful Agile implementation at scale. Their approach includes:
- Squad Model: Small, autonomous teams (6-12 people)
- Tribe Structure: Collections of squads working in related areas
- Minimal Hierarchy: Self-organizing teams with servant leadership
- Continuous Deployment: Multiple deployments per day
Results: Rapid feature development, high employee satisfaction, and market leadership in music streaming.
Netflix: Continuous Delivery Excellence
Netflix exemplifies Agile principles in their development practices:
- Microservices Architecture: Independent, deployable services
- Chaos Engineering: Proactive system resilience testing
- Data-Driven Decisions: A/B testing for feature validation
- DevOps Culture: Development and operations team integration
Results: 99.95% uptime, rapid global expansion, and industry-leading user experience.
Amazon: Customer-Centric Agile Development
Amazon’s approach demonstrates Agile scalability:
- Two-Pizza Teams: Small, focused development teams
- Working Backwards: Starting with press releases before development
- Continuous Innovation: Rapid experimentation and learning
- Customer Obsession: All decisions driven by customer value
Results: Consistent innovation, market dominance across multiple sectors, and exceptional customer satisfaction.
Challenges in Implementing Agile SDLC and Solutions
Common Implementation Challenges
- Cultural Resistance
- Challenge: Teams resist changing from familiar traditional methods
- Solution: Gradual transition with comprehensive training and change management
- Lack of Customer Involvement
- Challenge: Customers unavailable for regular feedback sessions
- Solution: Dedicated product owners and user proxies
- Inadequate Technical Infrastructure
- Challenge: Legacy systems don’t support continuous integration/deployment
- Solution: Incremental infrastructure modernization and toolchain upgrades
- Scaling Agile Practices
- Challenge: Agile works well for small teams but struggles at enterprise scale
- Solution: Frameworks like SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) or LeSS (Large-Scale Scrum)
- Incomplete Agile Adoption
- Challenge: Organizations adopt Agile practices without embracing Agile mindset
- Solution: Executive sponsorship and comprehensive cultural transformation
Best Practices for Overcoming Challenges
- Start Small: Begin with pilot projects before organization-wide rollout
- Invest in Training: Comprehensive Agile education for all stakeholders
- Measure Progress: Use metrics to track Agile maturity and success
- Embrace Failure: Create psychological safety for experimentation and learning
Continuous Coaching: Ongoing support from experienced Agile coaches
Best Practices for Successful Agile SDLC Adoption
Organizational Best Practices
- Executive Support and Sponsorship
- Leadership commitment to Agile transformation
- Clear communication of Agile benefits and expectations
- Resource allocation for training and tools
- Cultural Transformation
- Foster collaboration and transparency
- Encourage experimentation and learning from failure
- Recognize and reward Agile behaviors
- Comprehensive Training Programs
- Role-specific Agile training for all team members
- Certification programs for key roles (Scrum Master, Product Owner)
- Ongoing coaching and mentoring
Team-Level Best Practices
- Cross-Functional Team Composition
- Include all necessary skills within the team
- Minimize dependencies on external teams
- Maintain stable team composition
- Effective Communication Practices
- Daily standups for synchronization
- Regular retrospectives for continuous improvement
- Transparent information radiators and dashboards
- Quality-Focused Development
- Definition of Done for all work items
- Automated testing and continuous integration
- Regular code reviews and pair programming
Technical Best Practices
- Continuous Integration and Delivery
- Automated build and deployment pipelines
- Feature flags for controlled releases
- Comprehensive monitoring and alerting
- Test Automation
- Unit tests for all code components
- Integration tests for system interactions
- End-to-end tests for critical user journeys
- Architecture and Design
- Modular, loosely coupled system design
- Documentation that evolves with the system
- Regular architecture reviews and refactoring
A well-structured project management plan for software development incorporating these best practices ensures successful Agile implementation.
Tools Used in Agile SDLC
Project Management and Collaboration Tools
JIRA
- Comprehensive issue tracking and project management
- Customizable workflows and dashboards
- Integration with development tools
- Advanced reporting and analytics
Trello
- Visual Kanban boards for simple project management
- Card-based work item tracking
- Team collaboration features
- Integration capabilities with other tools
Azure DevOps
- End-to-end development lifecycle management
- Integrated source control, build, and deployment
- Work item tracking and reporting
- Enterprise-scale capabilities
Development and Version Control Tools
Git and GitHub/GitLab
- Distributed version control system
- Branch-based development workflows
- Code review and collaboration features
- CI/CD pipeline integration
Jenkins
- Open-source automation server
- Continuous integration and delivery
- Extensive plugin ecosystem
- Scalable build infrastructure
Testing and Quality Assurance Tools
Selenium
- Automated web application testing
- Cross-browser and cross-platform testing
- Integration with CI/CD pipelines
- Support for multiple programming languages
SonarQube
- Static code analysis and quality gates
- Technical debt management
- Security vulnerability detection
- Code coverage reporting
Communication and Documentation Tools
Slack/Microsoft Teams
- Real-time team communication
- Integration with development tools
- File sharing and collaboration
- Video conferencing capabilities
Confluence
- Team collaboration and documentation
- Knowledge base creation and maintenance
- Integration with JIRA and development tools
- Template-based content creation
Effective custom software development services leverage these tools to deliver high-quality solutions efficiently.
Future of Agile Development in SDLC
Emerging Trends and Technologies
- AI-Powered Development
- Automated code generation and optimization
- Intelligent testing and bug detection
- Predictive analytics for project management
- AI-assisted requirement analysis
- DevSecOps Integration
- Security embedded throughout the development lifecycle
- Automated security testing and compliance
- Continuous security monitoring
- Shift-left security practices
- Cloud-Native Development
- Microservices and containerization
- Serverless computing architectures
- Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies
- Infrastructure as code practices
Evolution of Agile Practices
- Remote and Distributed Teams
- Virtual collaboration tools and practices
- Asynchronous communication methods
- Global talent pool utilization
- Timezone-aware project management
- Continuous Everything
- Continuous integration and deployment
- Continuous testing and monitoring
- Continuous feedback and improvement
- Continuous learning and adaptation
- Business Agility Beyond IT
- Agile principles applied to entire organizations
- Portfolio-level Agile management
- Business and IT alignment
- Customer-centric value delivery
Predictions for the Next Decade
The future of Agile development will see increased automation, enhanced collaboration tools, and deeper integration with business processes. Organizations that embrace these trends while maintaining Agile’s core values of collaboration, adaptability, and customer focus will continue to thrive in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
Conclusion
Agile Development SDLC represents a fundamental shift from traditional software development approaches, offering unprecedented flexibility, speed, and quality in software delivery. The iterative development approach, combined with continuous feedback and adaptation, enables organizations to respond quickly to market changes while delivering exceptional value to customers.
The benefits of Agile extend far beyond faster delivery times, encompassing improved quality, reduced risk, enhanced collaboration, and increased customer satisfaction. By understanding the phases, frameworks, best practices, and tools associated with Agile SDLC, organizations can successfully navigate their digital transformation journey.
Success in Agile software development life cycle implementation requires commitment from all levels of the organization, from executive leadership to individual team members. It demands a cultural shift toward collaboration, transparency, and continuous learning.
Agencies like 86 Agency play a crucial role in helping businesses implement Agile SDLC effectively. With their expertise, organizations can streamline development processes, adopt the best frameworks and tools, and maximize the value delivered to customers while staying ahead in a competitive digital landscape.
As we look toward the future, Agile principles will continue to evolve, incorporating new technologies and methodologies while maintaining their core focus on delivering customer value through collaborative, adaptive approaches to software development.
FAQs
1. How is Agile different from traditional SDLC?
The main differences between Agile and traditional SDLC include:
- Approach: Agile uses iterative cycles vs. linear sequential phases
- Flexibility: Agile easily accommodates changes vs. rigid requirement adherence
- Customer involvement: Continuous collaboration vs. limited interaction
- Delivery: Frequent releases vs. single final delivery
Risk management: Early identification vs. late discovery of issues
2. What are the phases of Agile SDLC?
The SDLC phases in Agile methodology include:
- Requirements Gathering: Continuous collection and prioritization of user stories
- Design: Evolutionary architecture and collaborative design sessions
- Development: Sprint-based coding with continuous integration
- Testing: Integrated testing throughout each iteration
- Deployment: Frequent, automated releases
- Maintenance: Ongoing monitoring, support, and enhancement
These phases repeat in cycles throughout the project, allowing for continuous improvement and adaptation.
3. What are the advantages of Agile SDLC?
The key advantages of Agile SDLC include:
- Faster time-to-market with working software delivered in weeks
- Higher quality through continuous testing and feedback
- Reduced risk via early problem detection and resolution
- Enhanced flexibility to adapt to changing requirements
- Improved customer satisfaction through regular collaboration
- Better team collaboration and communication
Increased transparency and project visibility
4. Which companies use Agile SDLC?
Many leading technology companies successfully implement Agile SDLC, including:
- Spotify: Uses squad model and minimal hierarchy
- Netflix: Implements microservices and continuous delivery
- Amazon: Employs two-pizza teams and customer-centric development
- Google: Utilizes iterative development and data-driven decisions
- Microsoft: Applies Agile at scale with Azure DevOps
- IBM: Implements enterprise Agile transformations
These companies demonstrate that Agile practices can be successfully scaled from small startups to large enterprises.
5. What tools are essential for Agile SDLC implementation?
Essential tools for Agile SDLC implementation include:
- Project Management: JIRA, Trello, Azure DevOps for work tracking
- Collaboration: Slack, Microsoft Teams for communication
- Version Control: Git, GitHub, GitLab for code management
- CI/CD: Jenkins, Azure Pipelines for automation
- Testing: Selenium, JUnit for quality assurance
- Documentation: Confluence, SharePoint for knowledge management
The specific tool selection depends on team size, project complexity, and organizational requirements.



